Artificial Intelligence or AI is reshaping and is transforming the world faster than any other technology. From enhancing business operations to pioneering new approaches in healthcare, retail, and entertainment, AI’s potential seems limitless. And as we edge closer to advanced forms of intelligence, such as Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), AI is evolving from a buzzword into a concrete reality that’s impacting every facet of our lives.
In this article, we’ll explore the vast world of artificial intelligence, covering everything from AI chatbots and generative AI to robotic applications and cutting-edge tools from companies like Microsoft and Apple. Let’s dive deep into the future of AI, its core technologies, applications, ethical considerations, and the transformative trends that are driving it forward.

Table of Contents
The Future of Artificial Intelligence: From AI Chatbots to Artificial General Intelligence and Beyond

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is one of the most revolutionary technologies of the modern age. Its applications have permeated virtually every industry, from healthcare and finance to retail and entertainment. As AI advances, so does our understanding of its vast potential and the challenges it presents. In this article, we’ll explore what artificial intelligence encompasses today, the strides being made toward Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), the latest tools like generative AI and AI chatbots, and what the future holds for this groundbreaking technology.

Understanding Artificial Intelligence: From Narrow AI to AGI

Artificial Intelligence is the science of enabling machines to perform tasks that would normally require human intelligence, including reasoning, decision-making, and language comprehension. At its core, AI is about creating smart machines that can interact, learn, and problem-solve.
AI is typically classified into two main categories:
- Narrow AI (Weak AI): The type of AI that’s currently most common, designed for specific tasks like AI chatbots and recommendation engines. Siri, Alexa, and customer support bots are all examples of Narrow AI, which operates within a set scope but lacks full autonomy.
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): AGI, also known as “strong AI,” is a more ambitious concept. It aims to create machines with cognitive capabilities equal to or greater than human intelligence, with the potential to carry out any intellectual task a human can. Although AGI is still under development, researchers are making strides toward this ambitious goal.

The Key Technologies Powering AI

AI is fueled by several core technologies that work together to make machines capable of understanding, reasoning, and learning. These technologies are the foundation of the applications we interact with every day.
- Machine Learning (ML): Machine Learning is a subfield of AI that enables systems to learn and improve based on experience. By feeding data into ML algorithms, systems can detect patterns and make decisions with minimal human intervention. Generative AI models, such as those in tools like Midjourney and Leonardo AI, are built on ML and capable of creating unique outputs, like images, text, or even audio.
- Deep Learning and Neural Networks: Deep Learning, a subset of ML, uses neural networks inspired by the human brain to process complex information. These neural networks consist of interconnected layers of nodes, enabling the system to identify patterns, make predictions, and recognize images or voice commands. It’s through deep learning that AI chatbots can generate responses that feel natural and human-like.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Natural Language Processing is the technology behind the text-based and speech-based interactions in AI systems. NLP enables machines to understand, interpret, and respond to human language, making it the foundation of AI chat and virtual assistant technology. Systems like ChatGPT, for instance, use NLP to understand and generate responses based on user input.

The Role of AI Chatbots: Transforming Communication

One of the most user-facing applications of AI today is the AI chatbot. From customer service to personal assistants, AI chatbots are becoming essential tools for businesses and consumers alike.
- How AI Chatbots Work: AI chatbots rely on NLP and ML to understand user intent, respond accurately, and maintain context across conversations. Tools like ChatGPT by OpenAI are designed to provide realistic and natural language interactions, making AI chatbots valuable in applications that range from e-commerce to education.
- AI Chatbots Online: Real-Time Assistance: The accessibility of AI chatbots online allows people to get instant help, whether they’re asking questions, seeking guidance, or troubleshooting issues. Unlike traditional support, these chatbots can handle multiple users simultaneously, leading to faster response times and improved customer satisfaction.

Applications of AI Chatbots

AI chatbots have found applications in several industries, including:
- Healthcare: Virtual assistants provide patients with symptom checkers, appointment scheduling, and general health information.
- Finance: AI chatbots help customers check account balances, manage transactions, and receive fraud alerts.
- Education: AI tutors guide students through learning materials, offer personalized feedback, and even help with test preparation.

Generative AI: Revolutionizing Creative Industries

- Generative AI is a type of AI designed to produce new content, from images to text. It’s changing creative fields by enabling rapid content creation that is high-quality and diverse.
- Midjourney and Leonardo AI: Popular tools like Midjourney and Leonardo AI exemplify generative AI’s creative potential. They use advanced ML algorithms to generate images, making them popular choices for artists, designers, and content creators who need quick, visually stunning assets.
- Impact on Creative Industries: In fields like advertising, design, and entertainment, generative AI has become invaluable. Content that once required hours or days to produce can now be generated in minutes, allowing companies to test different creative approaches rapidly and reduce production costs.

AI’s Impact Across Industries: Transforming the Modern World

Artificial Intelligence is not confined to a single industry; its impact is felt across many sectors, from healthcare and finance to retail and logistics.
Healthcare
In healthcare, AI is saving lives by enabling faster, more accurate diagnoses. AI-powered tools analyze medical images, detect diseases in early stages, and assist in drug discovery, dramatically reducing the time needed for these critical tasks.
- AI Diagnostics: Machine learning algorithms analyze X-rays, MRIs, and other medical scans to identify anomalies that may indicate cancer, fractures, or other conditions.
- Patient Care: Chatbots and virtual health assistants provide patients with reliable medical information and symptom assessments.
Finance
Financial institutions are leveraging AI to detect fraud, personalize customer interactions, and automate repetitive tasks. Artificial Intelligence applications in finance can perform complex calculations, assess credit risk, and even provide investment advice, helping customers make more informed decisions.
Retail and E-commerce
AI helps online retailers enhance customer experiences through recommendation engines, personalized advertisements, and AI-powered customer service. For example, when browsing a website, an AI chatbot online might assist you with product suggestions or help you make purchasing decisions.
Manufacturing and Robotics
AI’s role in manufacturing is largely focused on automation and optimization. Artificial intelligence robots are increasingly common in factories, where they handle tasks such as quality control, inventory management, and assembly. These robots operate autonomously, increasing efficiency and safety in industrial environments.

Key Players in AI Development: Microsoft, Apple, and OpenAI

Microsoft AI
Microsoft has made significant investments in AI, particularly through its Azure cloud platform. Microsoft AI services are integrated into tools like Office 365 and Windows, helping users work smarter. Recently, Microsoft’s collaboration with OpenAI has allowed for more advanced AI tools in business applications.
Apple AI
Apple focuses on Artificial Intelligence applications that prioritize user privacy. Siri, Face ID, and on-device machine learning models in iOS are designed to deliver seamless, personalized experiences. Apple’s approach emphasizes the balance between AI’s convenience and user control over data.
OpenAI
OpenAI has set the benchmark in conversational AI with its GPT models, especially ChatGPT. Their mission is to create general-purpose AI systems that are safe and accessible, and their language models are used in a variety of applications, from personal chatbots to business productivity tools.

AI in Robotics: Physical Intelligence Meets Digital Smarts

AI-driven robotics represents a fascinating convergence of digital intelligence and physical capability, enabling robots to undertake complex, dynamic tasks in a variety of real-world settings. This synergy is particularly impactful as it allows machines to operate in intricate environments, performing tasks that previously required human involvement or oversight. Today, AI in robotics is rapidly advancing, from autonomous drones navigating vast landscapes to robots in manufacturing plants and warehouses enhancing productivity.

AI Robots in Everyday Life

AI-powered robots are becoming integral to various industries, enhancing efficiency, safety, and precision. In warehouses and factories, robots use AI algorithms to handle inventory, manage stock, and even assemble products. These machines can work tirelessly in repetitive and hazardous tasks, reducing the risk of injury and freeing human workers for more complex roles.
In healthcare, AI-driven robots assist in surgeries, transport medical supplies, and even provide companionship to elderly or isolated individuals. In households, robots perform chores like vacuuming, lawn mowing, and security monitoring, blending seamlessly into daily life. These applications highlight how AI-powered robots are transforming both the workplace and home environments, making tasks more manageable, efficient, and safe.

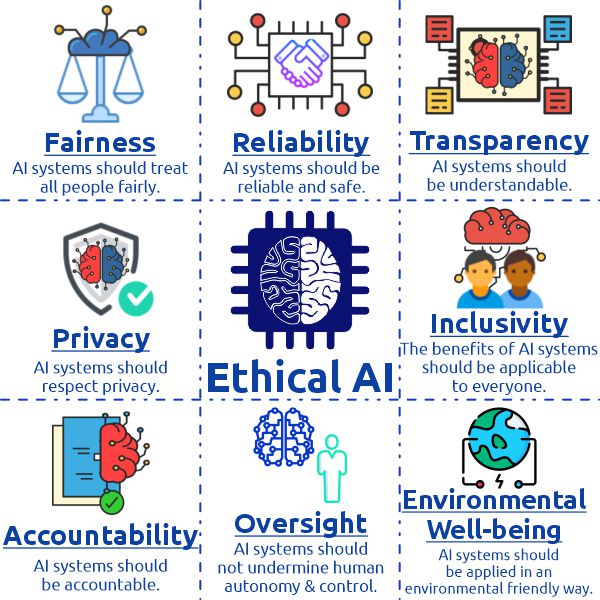
Ethical and Social Implications of AI

While artificial intelligence offers remarkable advantages, it also brings a host of ethical and social challenges. The impact of AI on society extends beyond technology and touches on privacy, fairness, job security, and accountability. Addressing these issues is critical to ensuring that AI’s benefits are broadly accessible, and its potential harms minimized.
Privacy Concerns

Artificial Intelligence systems rely heavily on data to function effectively, and in many cases, this data includes sensitive, personal information. From social media algorithms to personalized healthcare systems, AI gathers vast amounts of data to provide tailored services. However, the widespread use of personal data has raised concerns about privacy and consent. Often, users may not be fully aware of how their data is collected, used, or shared, creating a transparency gap that risks eroding trust.
Protecting privacy in an AI-driven world means implementing robust data protection policies, giving users more control over their information, and making data practices transparent. Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are also establishing frameworks, like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, to enforce data protection standards. As AI continues to evolve, creating a balance between innovation and privacy will be crucial.

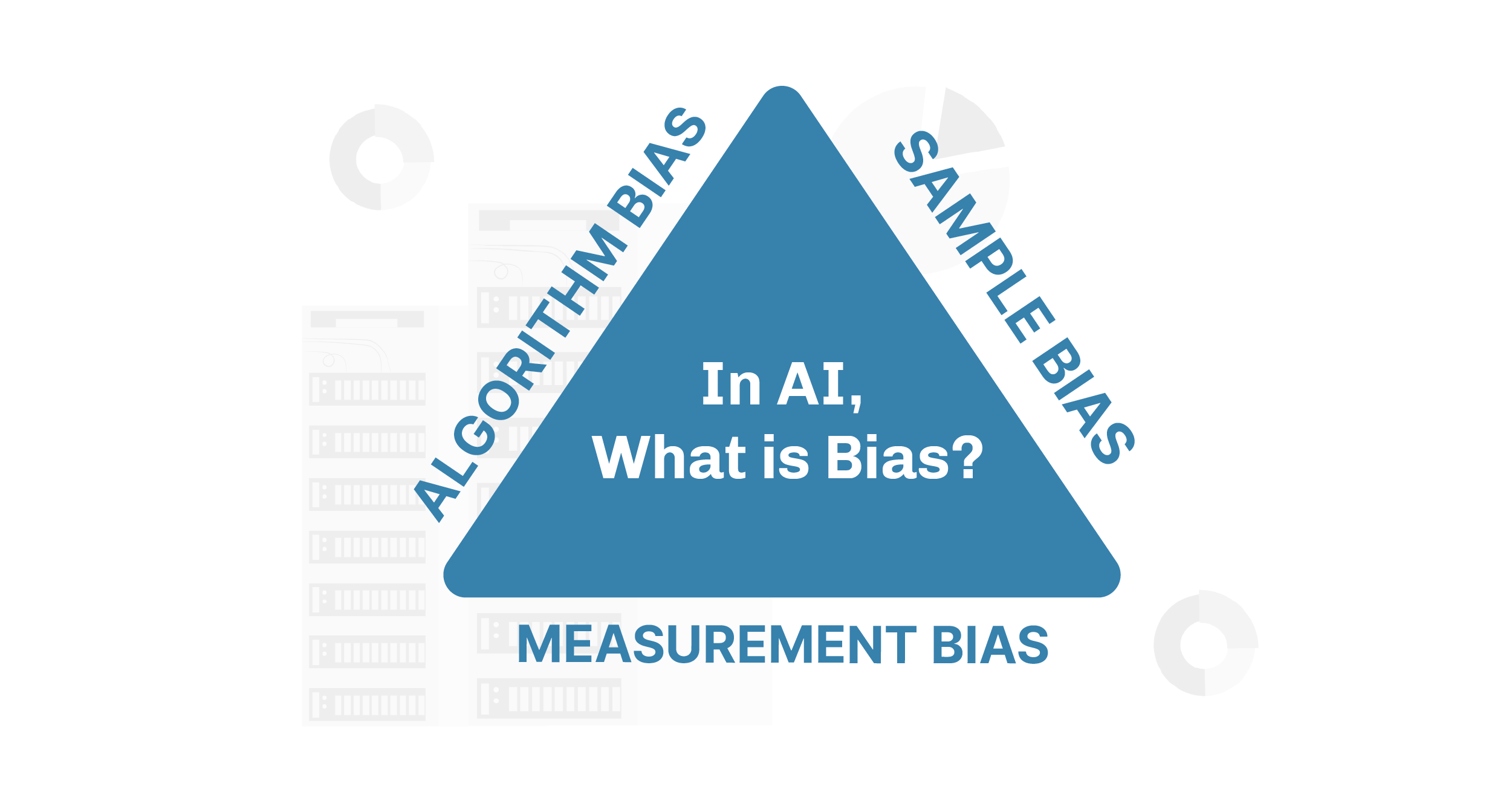
Bias in AI

Bias in AI models is a significant and complex challenge. AI systems learn from data, and if the training data includes biases, the AI will likely perpetuate them. This issue is particularly concerning in high-stakes fields such as hiring, law enforcement, and lending, where biased algorithms can have life-altering impacts.
For instance, if an AI system used in recruitment was trained on historical data biased against certain demographics, it may inadvertently favor candidates from particular groups, while unfairly disadvantaging others. Similarly, facial recognition technology has been shown to misidentify individuals from certain racial or ethnic groups at higher rates, raising concerns about fairness and discrimination.
To mitigate bias in Artificial Intelligence, developers are working to make models more transparent, traceable, and inclusive. Diverse and representative training data is critical, as is continuous auditing to identify and rectify biases. Techniques like explainable AI (XAI) also play a role by making AI decisions more interpretable, allowing stakeholders to understand the factors behind an algorithm’s choices.
Job Displacement

One of the most profound social implications of AI is its impact on the workforce. Automation and Artificial Intelligence are reshaping industries by taking over repetitive and routine tasks, from data entry and customer support to manufacturing and logistics. While this shift increases efficiency, it also threatens job security for those in positions susceptible to automation.
As AI continues to advance, several roles in sectors like retail, manufacturing, and transportation are at risk of becoming obsolete. In the long term, this trend could lead to a substantial workforce displacement, especially among low-skill jobs. For instance, self-checkout machines in retail and self-driving vehicles in logistics could lead to a decline in demand for cashiers and drivers.
However, while AI may displace certain jobs, it also has the potential to create new opportunities. History shows that technological advancements, while disruptive, often lead to the emergence of new roles and industries. The transition to an AI-driven economy will likely create demand for skills in AI development, machine learning, data analysis, and other specialized fields. Roles focused on the ethical and legal aspects of Artificial Intelligence, such as AI ethicists, will also become increasingly relevant.

Reskilling and Upskilling for an AI Future

Preparing the workforce for an AI-driven future will require significant investments in reskilling and upskilling. Governments, companies, and educational institutions all play vital roles in this transformation. Reskilling involves training individuals for entirely new types of roles, such as moving a worker from manufacturing into an IT support role, while upskilling focuses on enhancing the current skills of workers to include knowledge of new technologies relevant to their roles.
Initiatives like online learning platforms, vocational training, and AI literacy programs can equip workers with the skills needed in an AI-driven economy. For example, training programs on data analysis, machine learning basics, or even digital literacy can enable employees to transition into tech-related roles. Companies can also foster a learning culture by encouraging employees to stay updated with emerging technologies and trends.

Universal Basic Income (UBI) and Social Safety Nets

Some experts advocate for Universal Basic Income (UBI) as a way to cushion the impact of job displacement due to Artificial Intelligence. UBI is a model where citizens receive a regular, unconditional payment from the government, regardless of their employment status. Proponents argue that UBI could provide financial stability for individuals impacted by automation and AI, allowing them time to adapt, reskill, or seek new employment.
Social safety nets, such as unemployment benefits, retraining programs, and public healthcare, are also essential in ensuring that the benefits of AI do not come at the expense of economic security for vulnerable populations. By strengthening these systems, society can help workers transition smoothly in an evolving job market without sacrificing quality of life.

Building Ethical AI: A Collaborative Responsibility

To build AI systems that are fair, transparent, and accountable, stakeholders from all sectors must work together. Researchers, policymakers, businesses, and civil society each have a role to play in shaping the ethical development of AI.
- Researchers and Developers: Artificial Intelligence developers must prioritize ethics in the design and implementation of algorithms, actively working to identify and mitigate biases, and ensuring transparency and accountability in AI models.
- Businesses: Companies that use AI should be mindful of its social impact and incorporate ethical practices into their business models. They must be transparent about how AI is used in their products and services and how data is collected and managed.
- Policymakers: Governments play a crucial role in establishing regulatory frameworks that govern the ethical use of AI. By setting standards and creating oversight bodies, policymakers can help guide Artificial Intelligence development in a direction that aligns with public interest.
- Civil Society and Public Awareness: Civil society organizations can advocate for responsible AI practices and help raise public awareness of the ethical implications of AI. Educating the public about AI’s potential impact on society can foster a culture of accountability and empower individuals to make informed decisions.

The Future of Artificial Intelligence: Trends to Watch

As AI technology continues to advance, several key trends are shaping its future:
- AI and the Internet of Things (IoT): Integrating Artificial Intelligence with IoT allows for smarter devices that can interact autonomously, making everything from homes to cities more connected.
- Personalized Medicine: AI-driven precision medicine promises treatments tailored to an individual’s unique genetic makeup.
- Explainable AI (XAI): XAI aims to make Artificial Intelligence systems more transparent, allowing users to understand the reasoning behind AI decisions.
- AI in Space Exploration: AI is paving the way for autonomous exploration, helping space agencies navigate the vast and unknown realms of space.

Conclusion: Embracing an AI-Driven Future

The journey of artificial intelligence is far from over. As the technology matures, it will unlock even more groundbreaking possibilities that touch every aspect of human life. From improving healthcare outcomes to transforming global businesses, AI’s impact on society is profound. However, as we march forward, it’s crucial to develop and deploy Artificial Intelligence responsibly, ensuring that its benefits are accessible, and its risks minimized. Artificial intelligence offers extraordinary possibilities, from transforming industries to solving complex global challenges. However, with such transformative power comes a responsibility to manage AI’s societal impact thoughtfully. Addressing ethical and social implications—such as privacy concerns, bias, job displacement, and transparency—is essential for creating AI that serves the broader public good.
By fostering collaboration among developers, businesses, governments, and communities, we can harness AI’s potential responsibly. The journey to ethical AI is a collective one, and by prioritizing fairness, accountability, and inclusivity, we can ensure that AI technology enhances human life without compromising our values.
AI is no longer a futuristic dream. It’s here, transforming our world every day, and as we continue to innovate and adapt, its potential to make life better is almost limitless.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the world with its transformative power. However, managing the societal impact of AI responsibly is crucial. Addressing ethical and social implications, including privacy concerns, bias, job displacement, and transparency, is essential. Collaboration among developers, businesses, governments, and communities is key to harnessing AI’s potential while prioritizing fairness, accountability, and inclusivity. By doing so, we can ensure that Artificial Intelligence technology enhances human life without compromising our values.
Checkout other Generative AI: Shaping The Future Of Creativity & Innovation for more such information.

References
Artificial Intelligence: A Guide for Thinking Humans by Melanie Mitchell
Applied Artificial Intelligence: A Handbook for Business Leaders by Mariya Yao, Adelyn Zhou and Marlene Jia
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning by Vinod Chandra S. S was published by PHI Learning in 2014.
Computer vision | Definition, Examples, Applications, & Facts | Britannica
What Is Artificial Intelligence? Definition and History of AI – Caltech Science Exchange



